
Now press Delete to remove the background. Since the Fuzzy Select tool works only on areas that are touching, you might find that parts of the background remain unselected.įor example, check the space between the legs or arms if your subject is a person (like in the above image). Of course, it depends on each image and how many color gradients are in the background. I found this is the most accurate way to select the entire background. Now, click again close to the edge of the previous selection and carry on. Then, slowly turn back until you reach the last point where you are satisfied, then let go. Click and drag the tool until it starts to select something you don’t want. You can also make the selection in parts. If it’s not behaving as expected, try clearing the selection and starting over by clicking on a different point. The starting point makes a big difference when using the Fuzzy Select tool. Make sure you enable Antialiasing and Draw Mask – this last one allows for a color overlay that shows you what’s being selected.Īlso, tick the Feathering option and select the Radius value depending on how much feathering you want.Ĭlick on the background, drag the cursor up or down, and check the overlay to see how the selection is going. On the tool options panel, you’ll find different settings that allow you to tweak how the Fuzzy Select tool works. Step 3: Adjust the Fuzzy Select Tool settings Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut by pressing the U key. You can do this by clicking on its icon on the toolbar (it’s the one that looks like a magic wand).

There, click Add Alpha Channel – this will allow you to leave a transparent background once you delete the unwanted background. That would be preferably PNG, but GIF would work as well.Start by right-clicking on your image layer to open its menu. to a file format which supports transparency. įinally, export the transparent image with File → Export As. Once the desired transparency area is selected, simply hit. When this happens, use +Drag with a Select tool of your choice to select a subtractive selection area. In this case, and barely visible, nine desired pixels in the middle of the pipe were also selected for deletion.

Some of the desired image area might be selected as well because the colour matched. In between, hit + to undo.Īt times, it proves difficult to get the colour selection exactly right. Again, run a few tries while adjusting Threshold for best results. Nonetheless, do experiment with these settings and choose what looks best. For this particular example I chose not to apply Antialiasing nor Feather edges. This time around, do select Fill transparent areas as well as Sample merged.
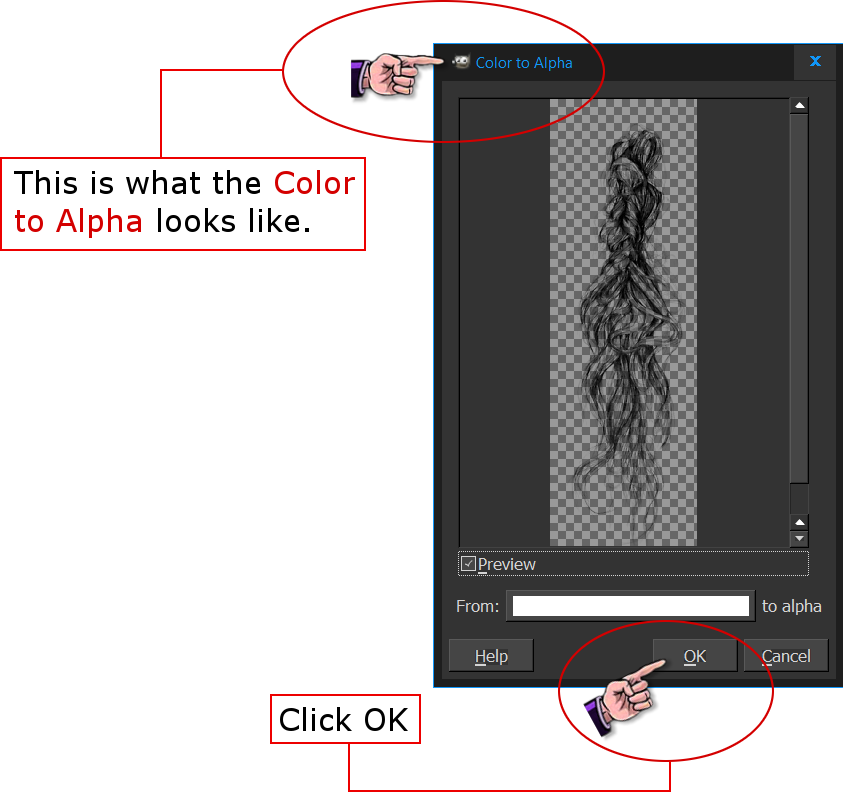
It might be tempting to perform Colour to Transparency, however this would also change semi-transparent areas within the desired image area. The right thing to do now is Select → By Colour. However, one can also use the eyedropper tool to pick a colour from anywhere on the desktop. Here, I used f3f3e9 as a background colour for plain colour filling. (In this respect, Adobe Photoshop is no different.) Hence, choose a colour which is compatible with the background on which the resulting picture will eventually be used.Ĭlick on the background colour rectangle in the upper half of the Tool Options toolbox window to change the background colour. Some colour mixing will be inevitable and even desired. Do select BG colour fill and Sample merged and run a few tries while adjusting Threshold for best results. Within the Bucket Fill toolbox options, select Fill transparent areas only when necessary. The next step is optional and consist in filling the area that should become transparent with a plain colour. This is done by selecting Layer → Tranparency → Add Alpha Channel. If this is the case, add an alpha transparency channel. Some image types lack a transparency channel JPG for example.
Note: This tutorial is also available in PDF.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
